Apple Watch: Patent shows how blood pressure will be measured in the future


The Watch Series 8 and Watch Ultra were launched alongside new features. But among those notably missing is the blood pressure system. Apple might have a reason for delaying the feature. Coincidentally, a new patent has been spotted showing a possible system design and how it could be integrated on Apple's watches.
The recent filing was published by the US Trademark office and was shared by Patently Apple. While the patent is partially related to the previous blood pressure monitoring system shared earlier, this particular method details a non-invasive device built to the strap of an Apple smartwatch or a separate cuff.
Non-invasive and non-inflating blood pressure reading on Apple Watch
What's interesting is that the wrist-worn device is composed of an array of non-inflating sensing units. It enables reading of the blood pressure changes in the user's veins using two sets of values or waves. These values are then superimposed on the main pressure wave to produce a final value, in this case the blood pressure reading.
In contrast, this is very different to the older patent that relies on an inflatable component. However, it is closer to pulse wave analysis used by Samsung on its Galaxy Watch 5 and Watch 5 Pro (review) wearables. Unfortunately, we cannot tell how the accuracy of this is compared to the current blood pressure system.
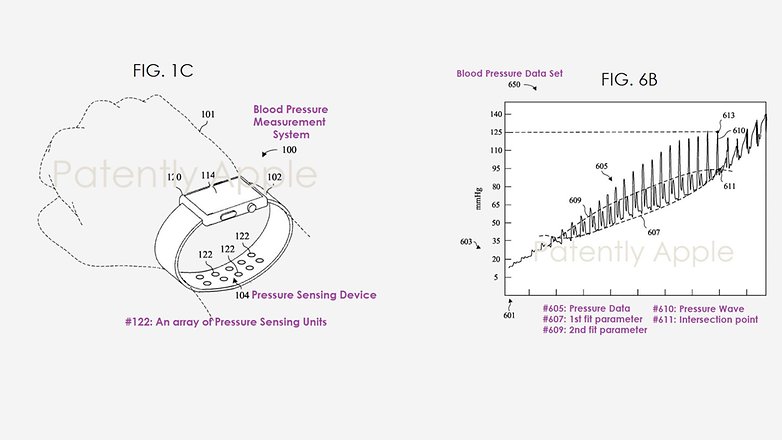
The other method discussed is using an arm band with an inflatable cuff and similar to the traditional monitoring system done by applying external pressure to the arm to detect changes in pressure. Crucially, the data gathered on both methods are either sent to an Apple Watch or iPhone.
So far, we have seen the unique designs of Apple's blood pressure monitoring system. The only missing piece if which of these will be utilized on an actual Apple watch. Do you think the upcoming Watch Series 8 or Watch Ultra 2 should add blood pressure reading?
Source: Patently Apple